U.S. EPA has amended tolerance exemption regulations of Cyflumetofen, Tetraniliprole, Cyantraniliprole, Afidopyropen, Spiromesifen, and MetamitronBy July 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has issued updates on the tolerance exemptions for six pesticides under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA). REACH24H has summarized for your convenience: 1. Cyflumetofen (Publication and Effective Date: 05/10/2024)
Cyflumetofen is an acaricide used to control mites on various crops, including fruits and vegetables. It specifically targets mite species while being safe for beneficial insects.This regulation establishes tolerances for residues of cyflumetofen in or on the following raw agricultural commodities:
- berry, low growing, subgroup 13-07G (0.6 ppm)
- fruit, small, vine climbing, except fuzzy kiwifruit, subgroup 13-07F (0.6 ppm)
- vegetable, cucurbit, group 9 (0.3 ppm)
- Adding in alphabetical order an entry for “Berry, low growing, subgroup 13-07G”;
- Removing the entry for “Cucumber (0.3 ppm)”;
- Adding in alphabetical order an entry for “Fruit, small, vine climbing, except fuzzy kiwifruit, subgroup 13-07F”;
- Removing the entries for “Grape (0.60 ppm)” and “Strawberry (0.6 ppm)”; and
- Adding in alphabetical order an entry for “Vegetable, cucurbit, group 9”.
 Source: Federal Register
2. Tetraniliprole (Publication and Effective Date: 05/15/2024)
Source: Federal Register
2. Tetraniliprole (Publication and Effective Date: 05/15/2024)
Tetraniliprole is an insecticide used against a variety of pests, including caterpillars and beetles. It disrupts the normal function of ryanodine receptors in the pests, leading to muscle contraction and death.This regulation establishes tolerance for residues of tetraniliprole in or on tea, dried at 80 ppm. In § 180.709, EPA amended Table 1 to Paragraph (a) by adding in alphabetical order an entry “Tea, dried” to read as follows:
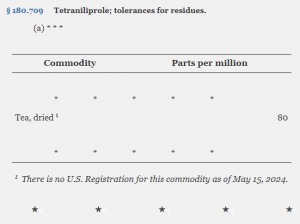 Source: Federal Register
3. Cyantraniliprole (Publication and Effective Date: 05/15/2024)
Source: Federal Register
3. Cyantraniliprole (Publication and Effective Date: 05/15/2024)
Cyantraniliprole is an insecticide that targets a broad spectrum of chewing and sucking pests. It works by activating ryanodine receptors in pests, leading to muscle paralysis and death.This regulation establishes and modifies tolerances for residues of cyantraniliprole, including its metabolites and degradates, in or on multiple commodities:
- herb, dried leaves, subgroup 25B at 150 ppm
- herb, fresh leaves, subgroup 25A at 40 ppm
- hop, dried cones at 70 ppm
- papaya at 1.5 ppm
- spice crop group 26 at 80 ppm
- vegetable, legume, bean, edible podded, subgroup 6-22A at 2 ppm
- vegetable, legume, bean, succulent shelled, subgroup 6-22C at 0.3 ppm
- vegetable, legume, forage and hay, except soybean, subgroup 7-22A at 40 ppm
- vegetable, legume, pea, edible podded, subgroup 6-22B at 2 ppm
- vegetable, legume, pea, succulent shelled, subgroup 6-22D at 0.3 ppm
- vegetable, legume, pulse, bean, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6-22E at 1 ppm
- vegetable, legume, pulse, pea, dried shelled, subgroup 6-22F at 1 ppm
- vegetable, foliage of legume, except soybean, group 7A at 40 ppm
- vegetable, legume, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6C at 1.0 ppm
- vegetable, legume, edible podded, subgroup 6A at 2.0 ppm
- vegetable, legume, succulent shelled, subgroup 6B at 0.20 ppm
- avocado at 0.4 ppm
- grape, table at 2 ppm
- mango at 0.7 ppm
- olive has been revised from 1.5 ppm to 3 ppm.
- olive, oil at 2.0 ppm has been removed.
- Adding the table heading “Table 1 to Paragraph (a)”;
- Adding in alphabetical order the entries “Avocado 2”; “Grape, table2 ”; “Herb, dried leaves, subgroup 25B”; “Herb, fresh leaves, subgroup 25A”; “Hop, dried cones”; and “Mango 2 ”;
- Revising the entry for “Olive 1”;
- Removing the entry for “Olive, oil 1”;
- Adding in alphabetical order the entries “Papaya”; and “Spice crop group 26”;
- Removing the entry for “Vegetable, foliage of legume, except soybean, group 7A”;
- Adding in alphabetical order the entries “Vegetable, legume, bean, edible podded, subgroup 6-22A”; and “Vegetable, legume, bean, succulent shelled, subgroup 6-22C”;
- Removing the entries for “Vegetable, legume, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6C”; and “Vegetable, legume, edible podded, subgroup 6A”;
- Adding in alphabetical order the entries “Vegetable, legume, forage and hay, except soybean, subgroup 7-22A”; “Vegetable, legume, pea, edible podded, subgroup 6-22B”; “Vegetable, legume, pea, succulent shelled, subgroup 6-22D”; “Vegetable, legume, pulse, bean, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6-22E”; and “Vegetable, legume, pulse, pea, dried shelled, subgroup 6-22F”; and
- Removing the entry for “Vegetable, legume, succulent shelled, subgroup 6B”.

 Source: Federal Register
4. Afidopyropen (Publication and Effective Date: 06/20/2024)
Source: Federal Register
4. Afidopyropen (Publication and Effective Date: 06/20/2024)
Afidopyropen is an insecticide used to control sucking pests such as aphids and whiteflies. It works by disrupting the feeding behavior of these pests, providing effective control with low toxicity to beneficial insects.This regulation establishes a time-limited tolerance for residues of afidopyropen, including its metabolites and degradates, in or on strawberry at 0.3 ppm. This tolerance expires on December 31, 2027. In § 180.700, EPA added Paragraph (b) to read as follows:

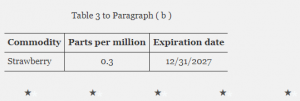 Source: Federal Register
5. Spiromesifen (Publication and Effective Date: 06/26/2024)
Source: Federal Register
5. Spiromesifen (Publication and Effective Date: 06/26/2024)
Spiromesifen is a pesticide primarily used to manage mites and whiteflies. It inhibits lipid biosynthesis, which is essential for the development and reproduction of these pests.This regulation establishes tolerances for residues of spiromesifen in or on orange at 0.15 ppm and orange subgroup 10-10A, oil at 10 ppm. In § 180.607, EPA amended the table in Paragraph (a)(1) by:
- Adding the table heading “Table 1 to Paragraph (a)(1)”; and
- Adding in alphabetical order the entries “Orange”; and “Orange subgroup 10-10A, oil”.
 Source: Federal Register
6. Metamitron (Publication and Effective Date: 07/10/2024)
Source: Federal Register
6. Metamitron (Publication and Effective Date: 07/10/2024)
Metamitron is a herbicide used to control a wide range of broadleaf weeds and grasses, particularly in sugar beet cultivation. It acts by inhibiting photosynthesis in susceptible plant species.This regulation establishes a time-limited tolerance for residues of metamitron, (4-amino-3-methyl-6-phenyl-1,2,4-triazin-5(4 H)-one), in or on the raw agricultural commodity (RAC) beet, sugar, roots at 0.01 ppm. This tolerance expires on December 31, 2027. U.S. EPA added § 180.726 to Subpart C to read as follows:
 Source: Federal Register
These updates reflect the U.S. EPA’s ongoing efforts to manage pesticide use and ensure safety in agricultural practices. For detailed information on each pesticide and the specific changes, please refer to the Federal Register notices linked below:
Cyflumetofen | Cyantraniliprole | Tetraniliprole | Afidopyropen | Spiromesifen | Metamitron
Source: Federal Register
These updates reflect the U.S. EPA’s ongoing efforts to manage pesticide use and ensure safety in agricultural practices. For detailed information on each pesticide and the specific changes, please refer to the Federal Register notices linked below:
Cyflumetofen | Cyantraniliprole | Tetraniliprole | Afidopyropen | Spiromesifen | Metamitron
Regulatory Background
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency), FFDCA (Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act), and CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) are closely related in the U.S. legal and regulatory framework:
- EPA is a federal agency responsible for protecting human health and the environment from the impacts of pollutants. EPA develops and enforces regulations related to environmental protection, including provisions concerning chemical safety and environmental impact assessments.
- FFDCA is a federal law enacted in 1938 that gives the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) the authority to oversee the safety and efficacy of food, drugs, and cosmetics, as well as medical devices.
- CFR refers to the collection of federal regulations in the United States, detailing rules and guidelines established by all federal government departments. Regulations from the EPA and FDA, among others, are detailed in CFR with specific terms and explanations.
- Pesticide Registration Improvement Act(PRIA)
- Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act(FIFRA)
Compliance Tips from REACH24H
1. Applicable Targets If you belong to the category of
- Crop production (NAICS code 111),
- Animal production (NAICS code 112),
- Food manufacturing (NAICS code 311),
- Pesticide manufacturing (NAICS code 32532),
Contact Us
REACH24H specializes in helping companies in the pesticide industry comply with global regulations. We offer various services, including registration, notification, data support, and compliance services, to keep companies informed about the latest regulatory developments and best practices.
- U.S. EPA Pesticide Registration
- Pesticide Risk Assessment
- GLP Study Monitoring
- QSAR
- Agrochemical Market Research & Regulation Compliance Report





