Hangzhou, China – September 12, 2025 –The 17th Chemical Regulatory Conference (CRAC China 2025), organized by REACH24H Consulting Group, was concluded in Hangzhou by the West Lake. Over two days, more than 400 representatives from governments, international organizations, industry, and academia highlighted green transition, regulatory innovation, and sustainable growth.
In addition to the main forum on "Global Chemical Management and Sustainable Development," the conference also featured several specialized sub-sessions, including "Global Pesticide Registration and Practical Innovation," "Recycled Plastics & Synthetic Resins Compliance," "Compliance Pathways for New Cosmetic Ingredients," "Customs Compliance — Import and Export Supervision and Trade Compliance". These sub-sessions provided a professional platform for attendees, offering focused discussions and fostering cross-sector collaboration and knowledge exchange.
Collaboration for Action: Turning Global Challenges into Solutions
Mr. Fangwei Hong, Chairman and CEO of REACH24H Consulting Group, noted that CRAC serves as a trusted bridge between policymakers, technical experts, and industry leaders. By creating space for dialogue, the conference helps transform complex global challenges into practical pathways for compliance, sustainability, and growth.

Sustainability, Circularity, and New Growth Strategies
EU Chemicals Strategy and Policy Under the New Leadership: Chemical Industry Action Plan
The European Union's "Chemical Industry Action Plan" highlights its commitment to sustainability, tackling key challenges such as industrial relocation, energy costs, and capacity overproduction. Mr. Geert Dancet, Secretary General of the Helsinki Chemicals Forum (HCF), outlined the four main objectives of the EU action plan: enhancing industrial resilience, securing energy supply while accelerating decarbonization, driving green innovation through market mechanisms, and simplifying regulatory frameworks. The plan is set to be reviewed in 2027, potentially leading to further simplifications in EU chemical regulations.

Empowering Chemical Sustainability with GreenScreen and Chemical Footprint
Economy Traditional product designs often lead to toxic residues and resource waste, complicating recycling efforts and exacerbating environmental pollution. The “Cradle to Cradle” (C2C) philosophy addresses this by distinguishing between "biological nutrients" and "technical nutrients," enabling continuous material cycles through multiple metabolic loops. This approach not only delivers ecological benefits but also creates commercial opportunities by driving ecological innovation.
Tools like GreenScreen and Chemical Footprint are playing a crucial role in helping businesses identify and replace high-risk substances, thus reducing environmental and health risks. These tools go beyond mere compliance; Mr. Chris Helt, Director of the GreenScreen Program at Clean Production Action, highlighted that they act not just as a "compliance shield" for businesses to meet regulatory requirements, but also as a "value engine" to unlock new market opportunities.

Pathways to Green Alternatives for Plastic Additives
Amid global plastic pollution challenges and China’s dual carbon targets, the plastic industry faces a significant transformation opportunity. Green alternatives to plastic additives are becoming crucial for industry upgrades and market competitiveness. Ms. Chen Yuan, Chief of the Regional Chemicals Management Branch, Basel Convention Regional Centre for Asia and the Pacific, emphasized that promoting green substitutes for plastic additives is not only a regulatory necessity but also a strategic move to capture the growing green market.

AI, New Productive Forces, and Industrial Transformation
AI technologies are reshaping traditional industry value chains by optimizing processes from smart manufacturing to digital twins. Mr. Zheng Qiang, “Qiushi” Distinguished Professor at Zhejiang University, discussed how AI’s “data-algorithm-computational power” synergy is driving industry transformation, emphasizing that this shift is a fundamental change in production organization rather than just an addition of technologies.

Product Carbon Footprint Accounting and Management
With climate change becoming a focal point globally, managing greenhouse gases has become a key aspect of corporate sustainability. In the chemical sector, product carbon footprints are now critical indicators in procurement and bidding, affecting corporate competitiveness. Mr. Ravinder Menon, Life Cycle Assessment Expert at Afton Chemical Corporation, explained that raw materials account for 75-90% of a product’s carbon footprint, and optimizing raw materials is the most effective way to reduce emissions. Afton’s use of life cycle assessment (LCA) tools in early product design led to the development of a new fuel additive with a 40% reduction in carbon footprint.

Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR): Expanding Scope to All Physical Goods
The European Union’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) has extended its scope beyond energy-related products to cover nearly all physical goods, with the aim of reducing both the carbon footprint and overall environmental impact throughout product lifecycles.
Mr. Julian Schenten, Senior Law and Policy Advisor at ClientEarth, presented key aspects of the ESPR, highlighting requirements on Digital Product Passports (DPPs), the phase-out of chemicals of concern, and measures to improve product durability and recyclability. Through practical case studies, he emphasized that the ESPR is not only a regulatory instrument but also a strategic response to sustainability challenges.

ESG in the Petrochemical Industry: Building a Strong Foundation for Sustainable Investment and Innovation
In China, as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) disclosure regulations tighten and capital markets increasingly favor sustainable investments, building a systematic ESG management framework has become a critical priority for businesses. Ms. Cui Zhibo, Manager of the Quality, Safety, and Environmental Protection Department at the China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, emphasized that ESG should be deeply embedded into various aspects of corporate governance, supply chain transformation, product design, and investor communication. She also shared examples from leading companies on carbon reduction targets, social responsibility, and board diversity.

Wanhua Chemical: Pioneering Green and Low-Carbon Transformation
As a leader in the global chemical industry, Wanhua Chemical has integrated its carbon neutrality goals into its corporate strategy and operations, pushing forward multidimensional carbon reduction practices through energy structure optimization, process innovation, and industry chain collaboration. Ms. Li Siyu, Carbon Management Manager of Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd, explained how the company uses technological innovation and industry chain collaboration to achieve precise carbon footprint management. Wanhua's practices demonstrate that green development can go hand-in-hand with economic benefits, showing that carbon reduction and market competitiveness can be achieved simultaneously through technology innovation and lean operations.

Regulatory Updates and Insights for Chemicals Compliance Management in Key Regions
Mr. Xiao Xuezhi, Chief Scientist with the Foreign Environmental Cooperation Center under China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment, served as the special session moderator. Guiding discussions on the core theme of Chemicals Compliance Management, Mr. Xiao led participants to explore the latest regulatory developments and practical strategies for industry response.

Elevating Global Governance: UN Launches ISP-CWP to Integrate Chemicals into Sustainability Agenda
In June 2025, the United Nations officially launched the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Panel on Chemicals, Waste, and Pollution (ISP-CWP), elevating global chemical governance to the same strategic level as climate change and biodiversity issues. This new platform aims to drive policy updates through authoritative scientific assessments. Programme Manager for China at the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Ms. Wang Qian, highlighted that businesses focusing only on passive compliance will face rising operational costs and market barriers. However, companies that actively pursue sustainable innovation—such as identifying alternatives and conducting life cycle assessments (LCA)—can gain significant competitive advantages in the marketplace.

China's Draft Environmental Code Sets New Mandatory Compliance Framework
Simultaneously, China has made pivotal strides in environmental governance. In April 2025, the country introduced the Draft Environmental Code, a significant milestone in environmental legislation. As noted by Mr. Bie Tao, Chief Legal Advisor to China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the Code formally establishes core systems for new chemical substance registration and environmental management. This move addresses previous shortcomings in regulatory enforcement and the low cost of non-compliance, pushing the concept of "green chemistry" from advocacy to mandatory compliance. The Code also provides a solid legal foundation for future legislation on chemical substance risk management and environmental control.

Implementing Lifecycle Management: China Builds Systemic Framework for Chemical Risk Prevention
China’s ongoing efforts to build a systematic, lifecycle-focused chemical management framework are progressing. Ms. Liu Hongying, Research Director of the Solid Waste and Chemicals Management Center, China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, elaborated on the latest policies and compliance requirements, helping companies establish robust environmental risk prevention mechanisms across R&D, production, and usage stages.

EU Reforms REACH and CLP to Reshape Chemical Strategy
2025 has emerged as a pivotal year in the evolution of Europe’s chemicals management framework. The European Commission, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and Member States are jointly advancing multiple regulatory reforms and new policy initiatives. These include updates to the CLP Regulation, adjustments to REACH administrative fees, ongoing development of the EU chemicals data platform, and the expansion of the list of restricted substances.
Ms. Catherine Cornu, Senior Scientific Officer at the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), emphasized that businesses must embrace proactive strategies to navigate these changes and secure their position in the green transition.

EU Enforcement Focuses on Imports and E-Commerce in 2024-25
Ms. Katja vom Hofe, Vice-Chair of the Forum for Exchange of Information on Enforcement (ECHA) and Legal Officer of Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of Germany(BAuA), pointed out that from 2024 to 2025, enforcement will focus on imports, e-commerce compliance, and integrated law enforcement. Companies need to stay informed about inspection guidelines, annual plans, and actively engage in seminars to develop effective compliance strategies.

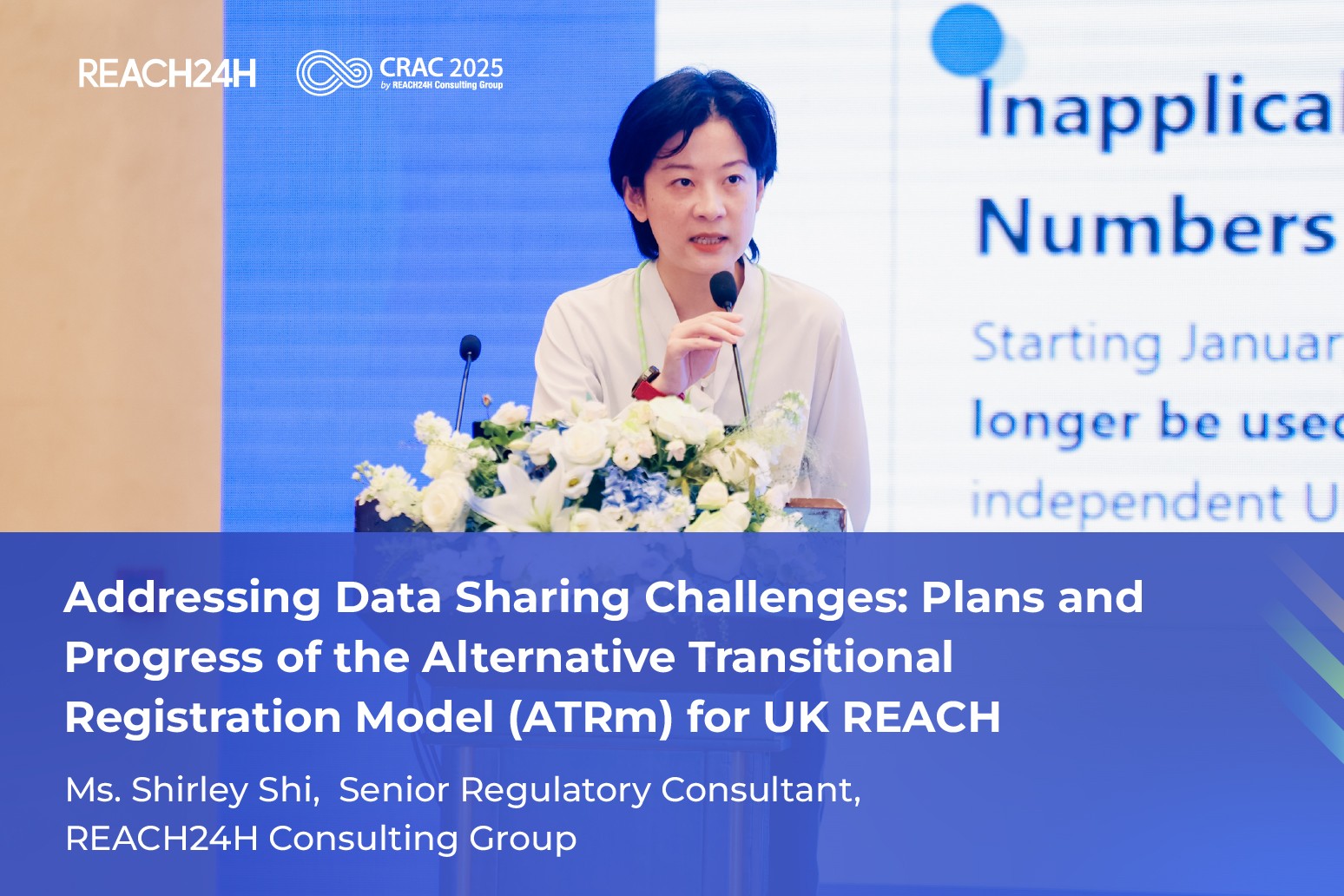
Navigating the UK REACH ATRm Delay: New Deadlines and Compliance Strategies for 2025
In July 2025, the UK’s Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (Defra) announced a public consultation on the UK REACH transition registration model. This new model will delay the originally scheduled registration deadline in October 2026, offering businesses a temporary relief from compliance pressure but introducing new regulatory uncertainties. Ms. Shirley Shi, REACH24H's Senior Regulatory Consultant, advised that businesses should take advantage of this buffer period to thoroughly understand the new requirements and create flexible strategies for continued market access.
Turkey Introduces Flexible Registration under Updated KKDİK
Turkey has also made strides in regulatory reform with the introduction of the KKDİK Regulation Implementation Procedures and Principles in August 2025. This new mechanism supports companies by allowing them to use existing global data for low-cost, phased registration, enabling production or import activities while completing full registration. Mr. Bektaş Kılıç, Chemical Engineer at the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change of Turkey, emphasized the pragmatic and flexible approach of this regulation.

Precise Regulation and Risk Prevention: South Korea Amends K-REACH and K-OSHA
South Korea passed significant amendments to the K-REACH and K-OSHA in July 2025, which focus on reclassifying hazardous substances and managing unknown risks while providing businesses with phased implementation to ease the transition. Ms. Jungsil Uhm, Head of the Environmental Training Division, Korea Environmental Conservation Institute, highlighted that these measures ensure public safety and environmental health while facilitating business adaptation.

Latest Customs Management & Global Supply Chain Restructuring in Vietnam
Vietnam is accelerating its efforts to enhance chemical management through revisions to the Chemical Law and related decrees, including Decree No. 33/2024/ND-CP and Decree No. 113/2017/ND-CP. These updates provide clearer guidelines on the lists of prohibited and restricted chemical substances for imports and exports. Mr. Tuan Thanh Le from the General Department of Vietnam Customs explained that the country is leveraging modern IT systems and a risk-based management approach to improve trade safety and clearance efficiency. Companies are advised to stay informed about the banned substances lists and ensure compliance with the country’s strict chemical regulations.

Mr. Do Thanh Bai, President of the Vietnam Responsible Care Council, recommended that multinational companies develop compliance strategies, embrace the trend toward environmentally friendly products, diversify their supply chains, manage risks, and invest in local technical capacity and talent development. This will help strengthen their competitive edge in Vietnam’s increasingly regulated market.

AI Driving Data Intelligence and Sustainable Transformation in the Chemical Industry
In 2025, China introduced its AI+ Initiative to accelerate the integration of artificial intelligence across major industries. For the chemical sector, this marks a shift from experience-based decision-making to data-driven intelligence, with AI being applied not only in isolated use cases but increasingly across entire industrial processes.
Mr. Zhu Haidong, AI Technology Expert at REACH24H, joined Mr. Shen Tao, Vice President of Strategy at FanRuan Software Co., Ltd., and Mr. Deliang Su, General Manager of Shanghai Haifan Technology Co., Ltd. Together, they explored three core themes: data-driven innovation, the role of private knowledge graphs in enhancing safety management, and future industry trends—sharing both practical applications and forward-looking insights on AI’s role in the chemical sector.

Looking Ahead
The successful conclusion of CRAC China 2025 reflects the strong commitment of regulators, enterprises, and research organizations to drive global cooperation on safer and greener chemicals management. The CRAC series will continue with upcoming editions in Japan and Singapore, further advancing industry dialogue and international collaboration on sustainability.
About CRAC
Since 2009, the Chemical Regulatory Annual Conference (CRAC) has brought together global forces for 17 consecutive years to build industry dialogue, invite global government agencies, industry experts, and business representatives to discuss global chemical management trends, exchange international advanced management experience, and extend to sub-sectors such as pesticides, disinfectants, cosmetics, food contact materials, pharmaceuticals, green and low-carbon sectors, and promote green, safe, and sustainable development of the industry, injecting new vitality into the benign development of the industry.
Over the years, CRAC has established partnerships with renowned institutions such as the Helsinki Chemicals Forum (HCF), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the European Commission (EC), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and more. Notably, CRAC has attracted distinguished global government agencies and associations to its events, including the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China, the Ministry of Emergency Management of China, the Ministry of Transport of China, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China, the European Chemicals Agency, the United States Environmental Protection Agency, the National Institute of Environmental Research of South Korea, and many other government agencies and organizations.
CRAC Organizer: About REACH24H
Established in 2009, REACH24H Consulting Group specializes in delivering comprehensive global market access services to companies operating in various sectors such as industrial chemicals, agrochemicals, disinfectants, cosmetics, food, packaging materials, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles.
Our diverse team comprises technical experts and international trade specialists based at our headquarters in Hangzhou, China, as well as branches in the US, the UK, Ireland, South Korea, Japan, and Singapore. Through strategic networking with businesses, associations, and government authorities across regions, we stay ahead of compliance needs, ensuring comprehensive solutions and proactive planning.
With a 24-hour global consulting service network and a team of technical experts, REACH24H helps enterprises and high-quality products take the initiative to trade, improving their understanding of technical barriers and assisting international trade departments and businesses to move from passive to active in the global market. Our extensive track record boasts successful assistance to over 15,000 companies worldwide, enabling them to navigate the global market seamlessly and bypass technical trade barriers.